The time command is linux is very much useful if you want to know the time information while running a program or a process.
The time command usage is as followsprompt $] time <commandname>
Example
prompt $] time ls
The output will be
real0m0.002s
user0m0.004s
sys0m0.000s
T S Pradeep Kumar
The time command usage is as followsprompt $] time <commandname>
Example
prompt $] time ls
The output will be
real0m0.002s
user0m0.004s
sys0m0.000s
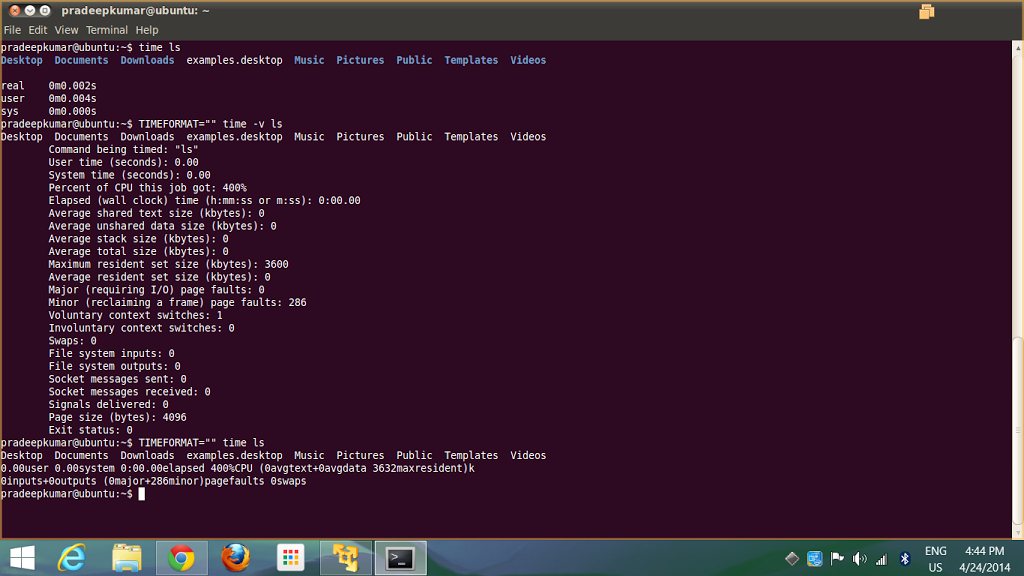
If you want to see the detailed system parameters occupied during a program or process, then the command will be
prompt$] TIMEFORMAT=”” time -v <commandname>
See the screenshot given below
 |
| Time Command in Linux |
The output of the above command is
Desktop Documents Downloads examples.desktop MusicPictures Public Templates Videos
Command being timed: “ls”
User time (seconds): 0.00
System time (seconds): 0.00
Percent of CPU this job got: 400%
Elapsed (wall clock) time (h:mm:ss or m:ss): 0:00.00
Average shared text size (kbytes): 0
Average unshared data size (kbytes): 0
Average stack size (kbytes): 0
Average total size (kbytes): 0
Maximum resident set size (kbytes): 3600
Average resident set size (kbytes): 0
Major (requiring I/O) page faults: 0
Minor (reclaiming a frame) page faults: 286
Voluntary context switches: 1
Involuntary context switches: 0
Swaps: 0
File system inputs: 0
File system outputs: 0
Socket messages sent: 0
Socket messages received: 0
Signals delivered: 0
Page size (bytes): 4096
Exit status: 0
Desktop Documents Downloads examples.desktop MusicPictures Public Templates Videos
Command being timed: “ls”
User time (seconds): 0.00
System time (seconds): 0.00
Percent of CPU this job got: 400%
Elapsed (wall clock) time (h:mm:ss or m:ss): 0:00.00
Average shared text size (kbytes): 0
Average unshared data size (kbytes): 0
Average stack size (kbytes): 0
Average total size (kbytes): 0
Maximum resident set size (kbytes): 3600
Average resident set size (kbytes): 0
Major (requiring I/O) page faults: 0
Minor (reclaiming a frame) page faults: 286
Voluntary context switches: 1
Involuntary context switches: 0
Swaps: 0
File system inputs: 0
File system outputs: 0
Socket messages sent: 0
Socket messages received: 0
Signals delivered: 0
Page size (bytes): 4096
Exit status: 0
Similarly, if a C or C++ program is compiled and linked to a file called helloc (the creation of helloc is given below)
prompt $] gcc -o helloc hello.c
or
prompt $] g++ -o helloc tspradeep.cc
if you want to execute this command
prompt $] TIMEFORMAT=”” time -v ./helloc
The time command will show you the memory page faults, context swtiching, swap memory used and other system parameters, etc.
If you have any added input for this command, let you write in the comment section.
Comments
Post a Comment