SUMO is the software that does the mobility of nodes, edges, etc from the MOVE software.
Installation of SUMO and MOVE in Linux is always a challenging job.
This post tells the installation of both these softwares SUMO and MOVE
Installation of SUMO
- In my case, I have used Fedora 19 (32 bit) OS. There are many problems in 64 bit version of Fedora 19, but 32 bit OS uses perfectly.
- Execute the command one by one.
- sudo yum update
- sudo yum install perl libFOX-1.6.so.0 libGLU.so.1 libgdal.so.1 libproj.so.0 libxerces-c-3.1.so (this will install almost 30 MB of softwares downloaded from the internet)
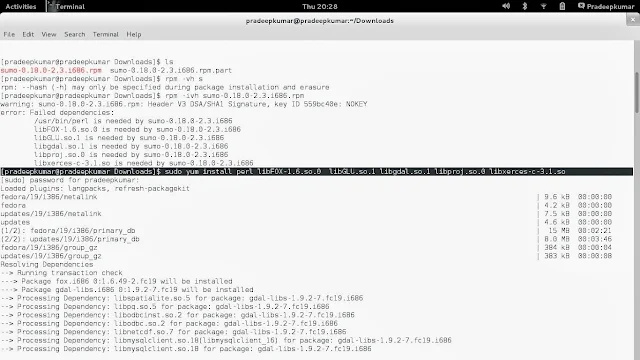 |
| Fedora 19 |
- Download the sumo software from http://download.opensuse.org/repositories/home:/behrisch/Fedora_19/i686/
- there will be SVN versions and source files, but you can download , sumo-0.18.0-2.3.i686.rpm
- Once downloaded, open the terminal and give this command to install SUMO
- sudo rpm -ivh sumo-0.18.0-2.3.i686.rpm (this will install the SUMO Software without any errors)
 |
| SUMO for VANET |
MOVE Installation
- Download the MOVE Software from this link http://lens1.csie.ncku.edu.tw/MOVE/download.php (you may fill your particulars to download the software)
- Once downloaded, execute this command in terminal to run the .jar file
- java -Xmx512m -jar MOVE.jar
- (this assumes that java is already there). For running MOVE.jar file, javac is not needed, just the java runtime environment is enough to run. Fedora 19 comes default installation of Java Run Time environment.
- Here is the screenshot after running the MOVE.jar file
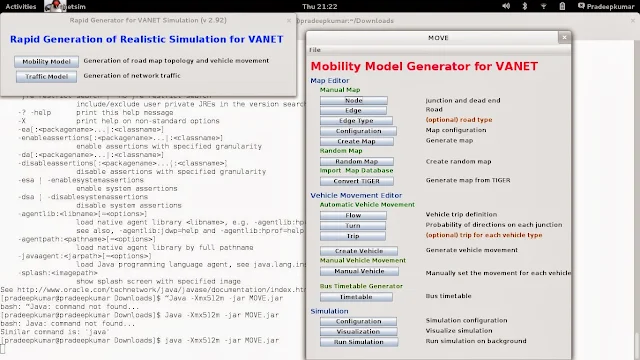 |
| MOVE Software in Fedora |
Comments
Post a Comment